What is Thermal Throttling CPU Best Guide How to Fix It 2024?
Do you want to know What is Thermal Throttling CPU? Thermal throttling is a mechanism employed by modern CPUs to protect themselves from overheating and potential damage.
When a CPU operates under high loads or in insufficient cooling conditions, it generates excessive heat, which can degrade its performance and even lead to permanent damage. In this article, we will delve into the concept of thermal throttling, explore its causes and effects, and discuss potential solutions to mitigate its impact on CPU performance.
What is Thermal Throttling CPU?
Thermal throttling is a safety feature built into CPUs to prevent overheating. When the CPU temperature surpasses a certain threshold, typically determined by the manufacturer, the processor reduces its clock speed or voltage to decrease heat generation.
Causes of Thermal Throttling
By throttling the CPU, the temperature is kept within safe limits, but this comes at the cost of decreased performance. The goal is to strike a balance between optimal performance and preventing potential damage. you can also read What is best CPU idle temp.
Causes of Thermal Throttling
Inadequate cooling solutions, such as a malfunctioning fan, blocked air vents, or improper heat sink installation, can lead to inadequate heat dissipation, causing the CPU to heat up quickly.
A. Insufficient cooling:
Inadequate cooling solutions, such as a malfunctioning fan, blocked air vents, or improper heat sink installation, can lead to inadequate heat dissipation, causing the CPU to heat up quickly.
B. High ambient temperatures:
Operating a computer in a hot environment can elevate the ambient temperature, making it more challenging for the cooling system to dissipate heat effectively.
C. Overclocking:
Overclocking a CPU involves running it at higher clock speeds than the manufacturer’s specifications, which results in increased heat generation. If the cooling system is not adequate to handle the additional heat, thermal throttling can occur.
D. Dust accumulation:
Over time, dust can accumulate on cooling components, inhibiting airflow and reducing their cooling efficiency. This buildup of dust can lead to increased temperatures and trigger thermal throttling.
Effects of Thermal Throttling
A. Reduced clock speed:
When thermal throttling occurs, the CPU automatically lowers its clock speed, resulting in decreased performance. Tasks that require significant processing power may experience slower execution times, affecting overall system responsiveness.
Related: What Is PC Bottleneck How To Fix It Complete Guide.
B. Increased latency:
As a result of reduced clock speed, the latency of CPU operations, including fetching, decoding, and executing instructions, is prolonged. This delay can impact tasks that require real-time responsiveness, such as gaming or multimedia applications.
C. Frame rate drops and stuttering:
In gaming scenarios, thermal throttling can cause a decline in frame rates and introduce stuttering. The CPU’s reduced processing power hampers its ability to keep up with demanding graphics rendering, resulting in a less smooth and immersive gaming experience.
D. System instability:
In extreme cases, thermal throttling may not be sufficient to prevent overheating, leading to system instability, random shutdowns, or even permanent damage to the CPU.
Mitigating Thermal Throttling

A. Efficient cooling solutions:
Ensuring proper cooling is essential to prevent thermal throttling. Upgrading the CPU cooler, cleaning dust from cooling components, improving case airflow, or using liquid cooling solutions can help dissipate heat more effectively.
B. Adequate case ventilation:
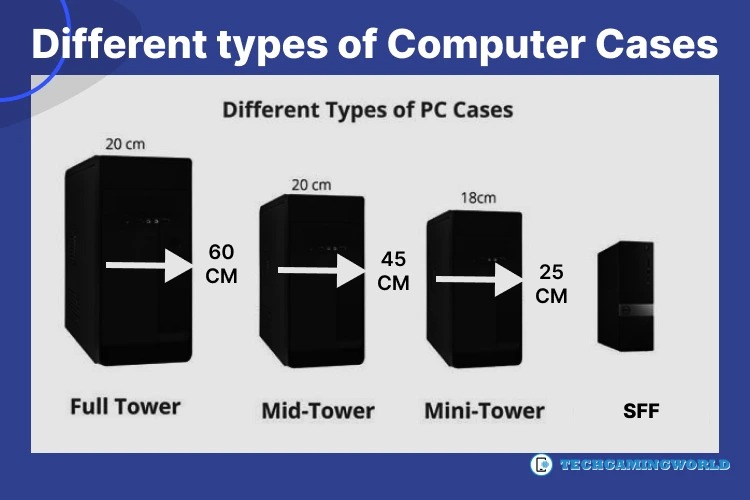
Proper airflow within the computer case is crucial to maintaining lower temperatures. Positioning case fans strategically, using dust filters, and maintaining cable management to optimize airflow can contribute to reducing CPU temperatures. Best Guide Different types of Computer Cases.
C. Thermal paste application:
Applying high-quality thermal paste between the CPU and the heat sink helps improve heat transfer, enhancing the cooling efficiency.
D. Balanced overclocking:
If you choose to overclock your CPU, it’s crucial to ensure a balance between increased clock speeds and adequate cooling. Overclocking should be accompanied by a robust cooling solution, such as a high-performance CPU cooler, to dissipate the additional heat generated effectively.

E. Monitoring software:
Utilizing software tools that monitor CPU temperature and performance can help identify potential thermal throttling issues. These tools provide real-time data and alerts,
allowing you to take prompt action if the CPU temperature exceeds safe limits.

F. System optimization:
Optimizing system settings and power management options can help minimize CPU load and reduce heat generation. This includes adjusting power profiles, closing unnecessary background applications, and optimizing software settings to distribute workload efficiently.

G. CPU Undervolting:
Undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to the CPU, which can help decrease heat generation and subsequently reduce the likelihood of thermal throttling. Undervolting should be done cautiously and with proper knowledge to avoid stability issues.
H. Proper case selection:
When building a system,
selecting a well-designed case with sufficient airflow and
compatibility with your cooling solution
can contribute to better heat dissipation
and reduce the chances of thermal throttling.
Conclusion
Thermal throttling is a protective mechanism implemented in CPUs to prevent overheating and potential damage. It reduces CPU performance to maintain safe operating temperatures. However, thermal throttling can have adverse effects on system performance, including reduced clock speed, increased latency, and instability. By employing preventive measures such as adequate cooling, efficient case ventilation, and system optimization, users can mitigate the risk of thermal throttling and maintain optimal CPU performance.
Here is your qeuestion What is Thermal Throttling CPU? Now clear. It is essential to strike a balance between performance and temperature management to ensure the longevity and reliability of the CPU in any computing system. So we hope you are now well aware of What is Thermal Throttling CPU or what is throttling cpu But if you want more information then comment in the comment section below.
FAQS

About Author
I am EDIE MILES, the founder of TechGamingWorld, a blog. in which is an online gaming community dedicated to providing the latest news and reviews about the world of online games, including PC and console games. Read More