PWM vs DC Fan Which One Is Best For PC Cooling? 2024
In this article we will discuss PWM vs DC Fan? In the realm of electronics and cooling systems, fans play a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures for various applications. When it comes to fan control mechanisms, two popular options stand out: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Direct Current (DC) fans.
While both serve the purpose of cooling, they possess distinct characteristics and offer unique benefits. In this article, we will delve into the differences between PWM and DC fans, exploring their working principles, advantages, and appropriate usage scenarios.
PWM vs DC Fan?
PWM stands for Pulse Width Modulation, which is a technique used to control the speed of electronic devices like fans. PWM fans have a dedicated control pin that receives varying pulses to adjust the fan speed. On the other hand, DC fans operate at a fixed speed based on the voltage supplied. PWM fans offer more precise control and can operate at lower speeds, reducing noise and energy consumption.

DC fans are simpler and often less expensive but lack the flexibility of PWM fans. The choice between PWM and DC fans depends on the specific requirements of the application, balancing cost, control precision, and performance needs.
TOP 3 PICKS
RANK
Image
Features
Price
Related: Is it Cheaper to Build a Gaming PC
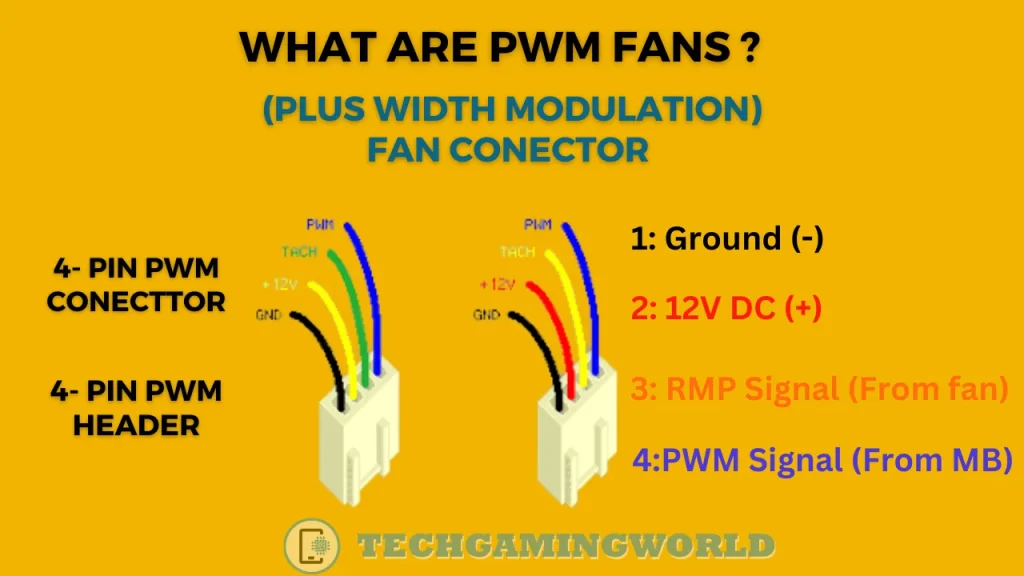
What Are PWM Fans?
PWM fans are a type of computer cooling fan that employs the Pulse Width Modulation technique to control their speed. PWM fans have an additional fourth wire, known as the PWM wire, which enables precise speed control. The other three wires typically include power, ground, and tachometer wires.
Comparison Table Between DC fans and PWM fans
| Aspect | PWM Fans | DC Fans |
|---|---|---|
| Speed Control | Precise control through Pulse Width Modulation | Fixed speed based on supplied voltage |
| Speed Range | Wide range, including low speeds for quiet operation | Limited range, may not support very low speeds |
| Noise Level | Can operate at lower speeds, reducing noise | Fixed speed may produce constant noise |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient at lower speeds | Consistent energy consumption |
| Cost | Typically more expensive | Generally less expensive |
| Control Flexibility | Can be easily adjusted or programmed | Limited control options |
| Complexity | Requires PWM controller or compatible motherboard | Simpler, no additional control requirements |

Working Principle of PWM Fans
The speed of a PWM fan is regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal. The fan’s control circuit receives the PWM signal from the motherboard or a fan controller and modulates the voltage applied to the fan’s motor accordingly. By rapidly switching the power on and off, the fan’s rotational speed is effectively adjusted.
Benefits of PWM Fans

Precise Speed Control:

PWM fans offer precise speed control, allowing for fine-tuning and customization of cooling performance. This feature is particularly valuable in scenarios where temperature fluctuations demand rapid adjustments in fan speed.
Enhanced Efficiency

PWM fans are more power-efficient compared to their DC counterparts. By controlling the duty cycle, PWM fans can operate at lower speeds when cooling demands are lower, thereby reducing power consumption and noise levels.
Related: You Can Also Read How to Turn Off Computer Fan.
Reduced Noise

PWM fans excel at noise reduction due to their ability to operate at lower speeds. By decreasing the fan’s rotational speed, PWM fans generate less noise, contributing to a quieter computing or cooling environment.
Overclocking Support

For computer enthusiasts and gamers who engage in overclocking, PWM fans prove to be advantageous. The precise speed control allows for effective cooling during intensive tasks, ensuring stable system performance.
What Are DC Fans?
DC fans, also known as voltage-controlled fans, are the traditional type of cooling fans widely used in various applications. These fans typically possess three wires: power, ground, and tachometer wires.
You can also read What is best CPU idle temp
Working Principle of DC Fans
DC fans operate by receiving a constant voltage supply, usually 12V or 24V. The speed of the fan is determined by the magnitude of the voltage supplied. A higher voltage results in a faster fan speed, while a lower voltage reduces the speed.
Benefits of DC Fans

Simplicity and Cost-effectiveness

DC fans are relatively simple in design and are available at affordable prices. They are suitable for applications where precise speed control is not a critical requirement, and a constant fan speed suffices.
Wide Compatibility

DC fans have been in use for a long time and are widely compatible with various cooling systems, appliances, and industrial equipment. Their ubiquity and ease of integration make them a popular choice in many scenarios.
Durability

DC fans are known for their robustness and long service life. Their design and construction focus on reliability, making them a reliable choice for applications that require continuous operation.
Low Minimum Speed

DC fans can operate at lower speeds compared to PWM fans. This feature is particularly beneficial in situations where a consistent low airflow is desired, such as in some industrial applications.

Conclusion
In the realm of cooling systems, both PWM and DC fans serve distinct purposes and offer unique advantages. PWM fans excel in applications that require precise speed control, enhanced efficiency, and reduced noise. They are particularly well-suited for computer enthusiasts, gamers, and scenarios where rapid adjustments in fan speed are necessary. On the other hand, DC fans are simple, cost-effective, and widely compatible, making them an excellent choice for applications that do not demand fine-tuning of cooling performance. So we hope you are now well aware of PWM vs DC Fan? But if you have more questions you can contact us via our comment section.

About Author
I am EDIE MILES, the founder of TechGamingWorld, a blog. in which is an online gaming community dedicated to providing the latest news and reviews about the world of online games, including PC and console games. Read More